Abstract
Introduction: Nivolumab (nivo) is an anti-PD-1 antibody that restores effective anti-tumor immune responses and is tolerable and effective in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (RR) classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). We previously reported results of PET-adapted sequential nivo +/- ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide) chemotherapy as first salvage tx in RR cHL, which was a safe and effective bridge to autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Here we present preliminary results of cohort B (non PET-adapted) of this trial, in which high-risk cHL patients all received nivo+ICE (NICE).
Methods: In cohort B of this prospective, multicenter trial, pts with biopsy-proven high-risk RR cHL after frontline treatment received 240mg nivo, and then starting 2 weeks later received 2-3 cycles of NICE (240mg nivo day 1, standard doses of ICE, administered inpatient or outpatient). High-risk RR cHL was defined as having one of the following: primary refractory cHL, relapse within 1 year of completing frontline therapy, B symptoms at relapse, extranodal disease at relapse, received brentuximab vedotin as part of initial therapy. PET-CT was performed after Nivo x 1 and NICE x 2; a third cycle of NICE was administered per discretion of the treating physician. Responding patients (complete response (CR) or partial response (PR)) were intended to proceed to ASCT. The primary endpoint was CR rate according to 2014 Lugano classification. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated using the Kaplan Meier method.
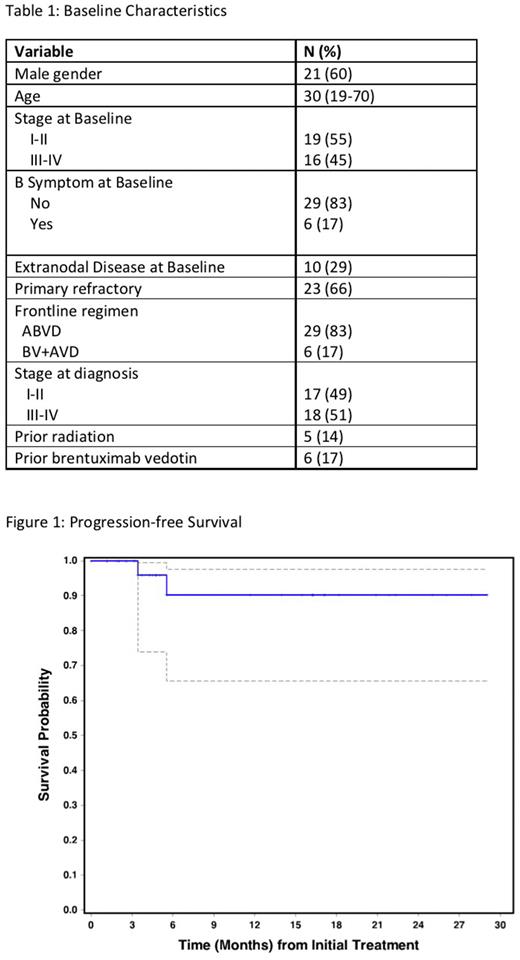
Results: 35 patients were enrolled, of whom 32 have completed the study treatment (3 remain in treatment). 34 patients were evaluable for toxicity; 32 were evaluable for response. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. Of patients completing the study treatment, 25 received 3 cycles in total (NICE x 2) and 7 received 4 cycles (NICE x 3). The overall response rate (ORR) was 100% with a CR rate of 88% (28/32). 29/32 patients who completed therapy have undergone ASCT. There were no stem cell mobilization/collection failures. The median time to neutrophil engraftment after ASCT was 11 days (range, 9-14) and median time to platelet engraftment was 11 days (range, 9-14). Of the 29 patients who have undergone ASCT to date, 7 (24%) have received post-ASCT consolidation (4 BV, 2 Nivolumab, 1 lenalidomide/ipilimumab) and 22 (76%) did not receive consolidation. Median follow-up was 12.8 months (range:0.5-29) and median post-ASCT follow-up was 12.5 months (range:0.3-25.6). 1-year PFS and OS for the entire cohort (n=34) was 90% (95% CI: 66-98) and 100% (95% CI: N/A), respectively (Figure 1). In patients who underwent ASCT directly after protocol therapy (n=22 with available data), 1-year PFS and OS were both 100% (95% CI:N/A for both).
The most common AEs (all grades) observed after the first nivo dose were hypertension (24%), fatigue (21%), and pruritis (15%), all of which were grade (gr) 1-2; no gr 3-4 events after nivo monotherapy were observed. The most common AEs (all grades) after NICE were anemia (65%), nausea (65%), fatigue (59%), hypertension (50%), sinus tachycardia (44%), and constipation (38%). The only non-hematologic gr 3-4 AE was gr 3 vomiting in one patient.
Conclusion: NICE is a well-tolerated and highly effective first salvage approach in pts with RR HL. In our cohort of high-risk patients, we observed high CR rates with excellent PFS after ASCT.
Disclosures
Mei:EUSA: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Incyte/Morphosys: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CTI: Honoraria; Beigene: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Lee:Cancer Experts: Honoraria; Aptitude Health: Honoraria; Octernal Therapeutics: Research Funding; Seagen: Research Funding; Curio Science: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Guidepoint Global: Honoraria; Deloitte: Honoraria; Pharmcyclics: Research Funding; Briston-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Korean Society of Cardiology: Honoraria; Olson Research: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Century Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Isufi:Kite: Speakers Bureau; Epizyme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Honoraria; BEAM Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Godfrey:Secura Bio: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Rosen:Exicure: Consultancy; PharmaGene, LLC: Consultancy; Apobiologix/Apotex Inc: Consultancy; Trillium Therapeutics, Inc: Consultancy; Verastem, Inc: Consultancy; NeoGenomics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pepromene Bio, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pepromene Bio, Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Exicure: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Pheromone Bio, Inc: Consultancy; January Biotech: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Trillium Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Herrera:Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Caribou: Consultancy; Gilead: Research Funding; Regeneron: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; KiTE Pharma: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Tubulis: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Adicet Bio: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Nivolumab - immunotherapy (checkpoint inhibitor). It is being tested in the 2nd line setting in conjunction with chemotherapy in this trial.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal